

For example, motorcycle racing engines can use compression ratios as high as 14.7:1, and it is common to find motorcycles with compression ratios above 12.0:1 designed for 95 or higher octane fuel.Įthanol and methanol can take significantly higher compression ratios than gasoline. Motorsport engines often run on high octane petrol and can therefore use higher compression ratios. The petrol-paraffin engine version of the Ferguson TE20 tractor had a compression ratio of 4.5:1 for operation on tractor vaporising oil with an octane rating between 55 and 70. Kerosene engines typically use a compression ratio of 6.5 or lower. The compression ratio may be higher in engines running exclusively on liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or "propane autogas") or compressed natural gas, due to the higher octane rating of these fuels.

Mazda's Skyactiv-D, the first such commercial engine from 2013, used adaptive fuel injectors among other techniques to ease cold start. Compression ratios are often between 14:1 and 23:1 for direct injection diesel engines, and between 18:1 and 23:1 for indirect injection diesel engines.Īt the lower end of 14:1, NOx emissions are reduced at a cost of more difficult cold-start. This can reduce efficiency or damage the engine if knock sensors are not present to modify the ignition timing.ĭiesel engines use higher compression ratios than petrol engines, because the lack of a spark plug means that the compression ratio must increase the temperature of the air in the cylinder sufficiently to ignite the diesel using compression ignition. Higher compression ratios can make gasoline (petrol) engines subject to engine knocking (also known as "detonation", "pre-ignition" or "pinging") if lower octane-rated fuel is used. Conversely, directly injected engines can run higher boost because heated air will not detonate without a fuel being present. Engines using port fuel-injection typically run lower boost pressures and/or compression ratios than direct injected engines because port fuel injection causes the air/fuel mixture to be heated together, leading to detonation. This is due to the turbocharger/supercharger already having compressed the air before it enters the cylinders. a turbocharger or supercharger) is used, the compression ratio is often lower than naturally aspirated engines. The 2014 Ferrari 458 Speciale also has a compression ratio of 14:1.Toyota Dynamic Force engine has a compression ratio up to 14:1.The SkyActiv engine achieves this compression ratio with ordinary unleaded gasoline (95 RON in the United Kingdom) through improved scavenging of exhaust gases (which ensures cylinder temperature is as low as possible before the intake stroke), in addition to direct injection.
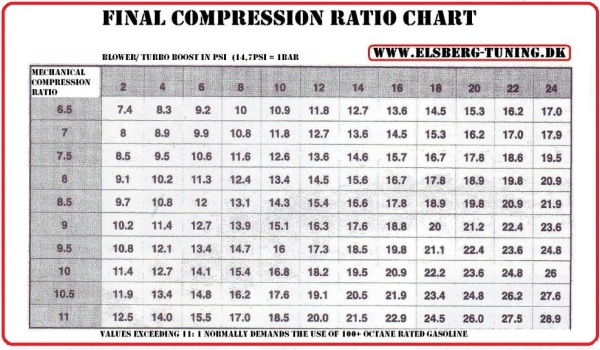
Some Mazda SkyActiv engines released since 2012 have compression ratios up to 16:1.Cars built from 1955–1972 which were designed for high- octane leaded gasoline, which allowed compression ratios up to 13:1.Several production engines have used higher compression ratios, including: In petrol (gasoline) engines used in passenger cars for the past 20 years, compression ratios have typically been between 8:1 and 12:1. This occurs because internal combustion engines are heat engines, and higher compression ratios permit the same combustion temperature to be reached with less fuel, while giving a longer expansion cycle, creating more mechanical power output and lowering the exhaust temperature. The dynamic compression ratio is a more advanced calculation which also takes into account gasses entering and exiting the cylinder during the compression phase.Ī high compression ratio is desirable because it allows an engine to extract more mechanical energy from a given mass of air–fuel mixture due to its higher thermal efficiency. The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.Ī fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the static compression ratio, calculated based on the relative volumes of the combustion chamber and the cylinder when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke, and the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at the top of its stroke. Static compression ratio is determined using the cylinder volume when the piston is at the top and bottom of its travel. JSTOR ( July 2019) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message).Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.įind sources: "Compression ratio" – news Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. This article needs additional citations for verification.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
